Here’s the part where they explain the theoretical solution
Under Oppenheim’s theory, however, space-time wouldn’t just be smooth, it would become sort of wobbly and unpredictable.
Here’s where it becomes testable. This wobbliness would result in fluctuations of measurable properties that are larger than the fluctuations predicted by quantum theory.
With the right experiment, physicists could look for those fluctuations.
We have shown that if space-time doesn’t have a quantum nature, then there must be random fluctuations in the curvature of space-time which have a particular signature that can be verified experimentally," says physicist Zach Weller-Davies of University College London.
“In both quantum gravity and classical gravity, space-time must be undergoing violent and random fluctuations all around us, but on a scale which we haven’t yet been able to detect. But if space-time is classical, the fluctuations have to be larger than a certain scale, and this scale can be determined by another experiment where we test how long we can put a heavy atom in superposition of being in two different locations.”
I think they don’t really do a good job of explaining it, so if anyone here knows more about it, please share!


On cooler news. We found out that our previous measurements on the acceleration of the universes expansion might have been entirely wrong
That is because the data could have been skewed by a rather recently discovered superstructure called the “Local Void” which the milky way galaxy itself borders to and has been obscured by our own galaxy. It’s very likely that the universe might not be expanding at an increasing speed after all of it turns out the “local void” skewed the data we have. We are in the middle of figuring THAT out!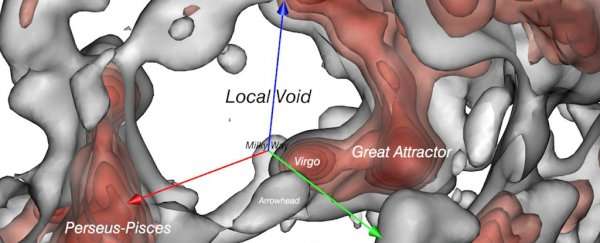
Can the universe even expand faster than the “speed of light”? Not saying anyone is claiming that, just a thought I had.
Yes because new space can be made faster then light.